The fuser command is used to identify which processes are currently have open files, directories, or sockets. is useful for troubleshooting scenarios when you need to find which process having a particular resource, such as a file or network socket.
- About fuser : Identify processes using files or sockets
- It comes from “psmisc-x.x” package.
- Configuration Files:
/proc location of the proc file system - Path: /sbin/fuser
Examples:
1. To get the process using root file system
| $ fuser -c / |
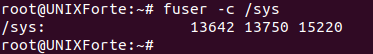
2. To show all files specified on the command line
| $ fuser -a / |
3. To kill the processes accessing the files
| $ fuser -k /tmp |
4. To ask the user before kill the process
| $ fuser -ki /tmp |
5. To list all the known signal
| $ fuser -l |
6. To list all processes of the mount point in which the given file is residing
| $ fuser -m /tmp/file.txt |
7. For silent operation
| $ fuser -s /tmp |
8. To specify the signal instead of SIGKILL
| $ fuser -signal 15 /tmp |
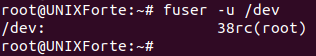
9. To get the user name of the process owner
| $ fuser -u /tmp |
10. To set the verbose mode
| $ fuser -v |
11. To display the version information
| $ fuser -V |
12. To search for only IPv4 sockets
| $ fuser -4 /tmp |
13. To search for only IPv6 sockets
| $ fuser -6 /tmp |
14. To reset the all the signal options
| $ fuser – |
Related Commands: kill, killall, lsof, ps, kill
fuser command not found
If you get a message that fuser command is not found then it means your system is not haaving the “psmisc” package installed on it. Follow below steps to install the package as per your respective OS version.
| OS Version | Command |
| RedHat / CentOS / Fedora | yum install psmisc |
| Debian / Ubuntu / Kubuntu | apt install psmisc |