In Linux operating systems fdisk command is used for disk partitioning. Which enables system administrator to create, delete, modify, and manage disk partitions on the system. It comes from util-linux-ng-x.x.x package.
Examples:
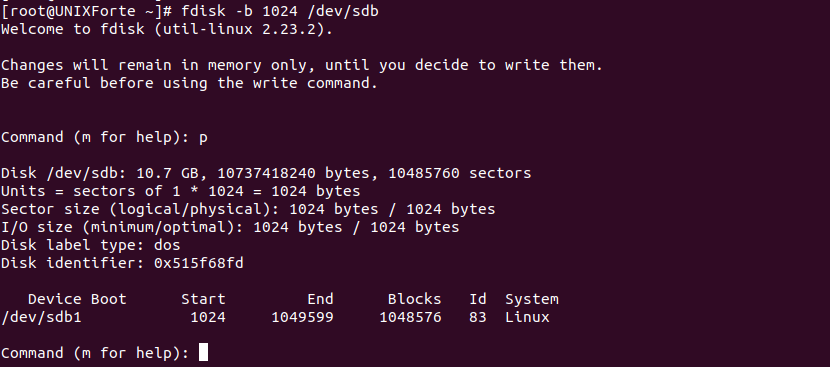
1. To set the sector size of a disk
| $ fdisk -b 1024 /dev/sdd |
2. To specify the number of cylinders of the disk
| $ fdisk -C 1024 /dev/sdb |
3. To Specify the number of heads of the disk.
| $ fdisk -H 1024 /dev/sdb |
4. To Specify the number of sectors per track of the disk.
| $ fdisk -S sects /dev/sdb |
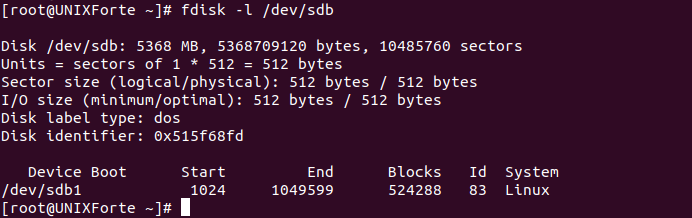
5. To list the partition tables for the specified devices and then exit
| $ fdisk -l $ fdisk -l /dev/sdb |
6. To get the size of a particular disk
| $ fdisk -s /dev/sdb |

7. To switch off DOS-compatible mode
| $ fdisk -c |
8. To get the help for fdisk
| $ fdisk -h |

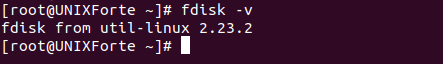
9. To get the version of the fdisk
| $ fdisk -v |
Related Commands: cfdisk, sfdisk, mkfs, parted, partprobe, kpartx
fdisk command not found
If incase while working on a Linux system, you receive a message that the “fdisk command not found”, that means the below package is not present or installed on system. Hence please follow below commands to install it.
| OS Version | Command to Install |
| RedHat / CentOS / Fedora | yum install util-linux-ng |
| Debian / Ubuntu / Kubuntu | apt install util-linux |